|
3.2.2 Signal Flow Graphs:
Frequency Domain Analysis You have now viewed signal flow graph representations for extracting energy, an important time-domain feature needed by the speech recognizer. As discussed, frequency-domain features are also needed by the recognizer. The signal flow graph below corresponds to the block diagram for the frequency domain example given in Section 3.1.3. Note that the block previously labeled Spectrum is shown as a component labeled Spec. This component represents the algorithm to be used for frequency spectrum analysis, such as a Fourier Transform. Click on any of the components in the graph for further details. 
While the Fourier Transform provides a valuable method for analying the frequency spectrum of a signal, additional methods are needed to fully measure the features needed by a speech recognizer. Mel-Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients (MFCC) are an example of a method that further analyzes the Fast Fourier Transform of the speech signal. The value of the method is attributed to its similarity to the functioning of the human auditory system. MFCC's use a mathematical transformation called the cepstrum which computes the inverse Fourier transform of the log-spectrum of the speech signal. The logarithmic nature of the technique is significant since the human auditory system perceives sound on a logarithmic scale above certain frequencies. The signal flow graph below includes a component labeled Ceps for cepstral analysis. Click on any of the components of the graph for further description. 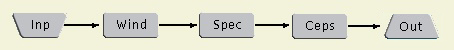
See the workshop notes on signal processing for a more detailed theoretical description. of MFCC's. |