A Quick Overview of Sof

First of all, what is Sof? Sof (Signal Object File), one of the most
attractive features of the IFCs, provides us with a way to simplify
and unify file I/O among all data objects in the IFCs. Sof also makes
it easy to represent files in either binary or text format. Each IFC
has the following methods: read, readData, write, and writeData. The read
method will, by
default, search a file for a tag corresponding to the name of its
class. If this tag is found, the read method proceeds to call the
readData method which is responsible for reading the actual object
member data from the file. The class's readData method calls the readData
methods of each of the class's member data (or whatever member data
we feel needs to be read from a file for a particular data object).
The write and writeData methods follow the same principle. In doing
this, we can nest as many data objects as we want in a class and not
increase the complexity of the I/O methods needed for that class.
Another convenient features of Sof is that read and write methods
have very little involvment in taking different actions for binary
and text file representations. Most of these decisions are made in
the Sof parser and the Sof class.
IHD (ISIP Hierarchical Digraph)

Early versions of our software only supported one language model
format, which we called Digraph. To store a language model to a
file, we used to write it's components, which were SearchLevel
objects, individually to the file instead of writing a single object.
SearchLevel objects were stored in a similar manner. Each of the
different components had a separate tag that identified the type
of component. Instead of using the traditional Sof 'read' and
'write' methods for LanguageModel object I/O, we used
the methods 'load' and 'store' to read and write the language model
components to and from a file. If we were to look at a text representation
of one of these files, there was no clear indication that the file
contained a language model.
Click here
to see an example.
This method of storing a language
model prevented the ability to store other data, besides the
language model data, to the file. For example, if we were to
create a new type of language model in the future that used
the original LanguageModel object as a data type, it would be
very difficult to store the new type of language model to a file.
Also, we may want to store multiple language models to a file, but
this method of storing prevented that as well.
|
|
As we begin to support multiple industry standard grammar formats
(JSGF, XML), we find that it's much more convenient to store a
self-contained LanguageModel Sof object to a file rather than
individual components. This way, we can use the power of Sof to
unify these different formats so that they may be easily read and
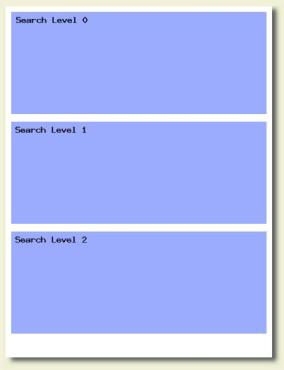
written. The image to the right illustrates how we now store a
LanguageModel object in IHD format. When LanguageModel's write
method is called, the system writes a LanguageModel tag and the
format of the language model, which is IHD in this case. The
system proceeds to write a HierarchicalDigraph object, which is
a class we use to encapsulate the vector of SearchLevel objects
that comprises the "guts" of the language model.
Click here
to see an example of the new IHD language model format. This
method of LanguageModel I/O eliminates the contraints set by the
previous method.
|

|
Converting to IHD

Don't worry, your old language model files aren't useless. If you
still have the native file created by network builder, all you need
to do is load the native file in network builder, and save the
file in IHD format. A tutorial for using isip_network_builder can
be found
here.
If you don't have the native language model, but you still have the
the old Digraph language model, you can convert to the new IHD format
using either isip_network_builder or isip_network_converter.
To use isip_network_builder, simply load the old file and save in
IHD format, just as you would do with native file. To convert
using isip_network_converter, use the following command:
isip_network_converter -input_format IHD -output_format IHD -output_type TEXT input_file output_file smp_file
You can also use DIGRAPH as the input format and IHD as the output
format. The output file will be in the new IHD format.
These changes will be included with our upcoming release, which is
scheduled for sometime this fall. If you'd like to check out the
most current (pre-released) version of our software, see the
tutorial
here.
|

