-
Phoneme Mappings
Most languages, including English, can be described in terms of
a set of distinctive sounds, or phonemes. In particular, for
American English, there are about 42 phonemes including vowels,
diphthongs, semi-vowels and consonants. The internationally
standard method to represent phonemes is International Phonetic
Alphabet
(
IPA).
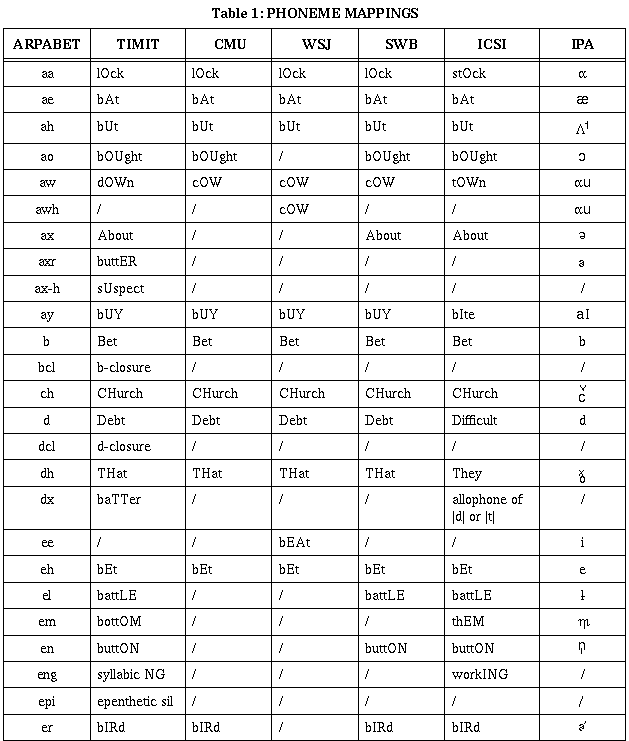
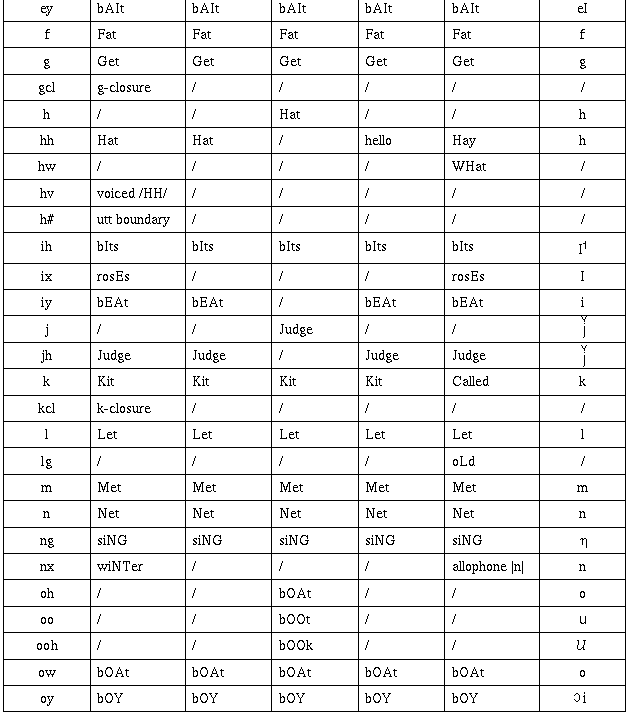
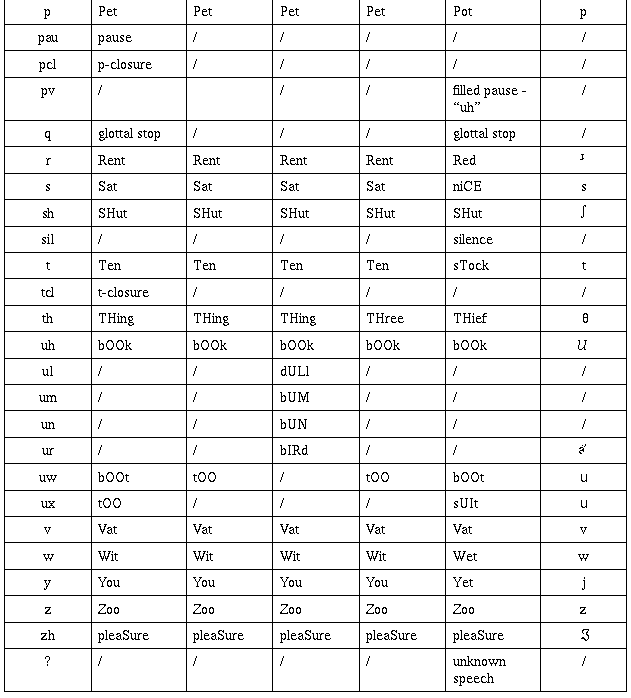
To enable computer representation of the phonemes, it is
convenient to code them as ASCII characters. Several schemes
have been proposed, e.g., ARPABET, TIMIT, CMU, WSJ and SWB. The
following table shows the mapping between these representations
and IPA.
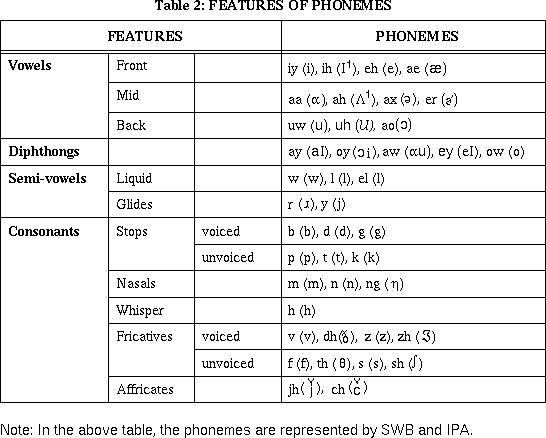
- Features of Phonemes
Phonemes can be classified in terms of distinct features, such as
vowels, consonants, etc.
-
References
- International Phonetic Alphabet,
http://www.arts.gla.ac.uk/IPA/ipa.html
- LDC TIMIT lexicon,
http://www.ldc.upenn.edu/doc/timit/phoncode.doc
- LDC PRONLEX Transcription,
http://www.ldc.upenn.edu/readme_files/comlex_pron.readme.html.
- The CMU Pronouncing Dictionary,
http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudic.
- Phoneme Classification,
http://www-dsp.rice.edu/courses/elec532/PROJECTS96/synthesis/phoneme_descriptions.html, Rice University
- ARPABET-IPA MAPPINGS,
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~laura/pages/arpabet.ps
- WordNet - a Lexical Database for English,
http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/~wn/
- Calvert, Donald R.
Descriptive Phonetics , Thieme Medical Publishers, 1992.



