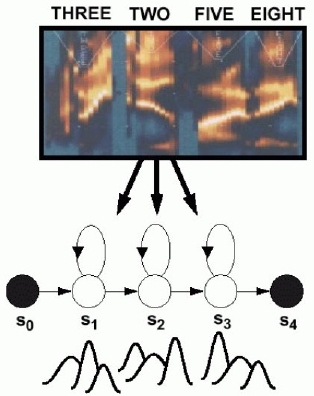
- Acoustic models encode the temporal evolution of the
features (spectrum).
- Gaussian mixture distributions are used to account
for variations in speaker, accent, and pronunciation.
- Phonetic model topologies are simple left-to-right structures.
- Sharing model parameters is a common strategy to reduce
complexity and avoid undertraining:
(39 features +
39 covariance values +
1 mixture weight) x
16 Gaussian per state x
3 states/phone x
80,000 CD phones =
~300 x 106 parameters!
|
|

