FAST FOURIER TRANSFORMS
The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is nothing more than a computationally
efficient version of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):
 The most common approach to achieving this efficiency is to use a
decimation-in-time strategy that benefits from the non-linear
computational complexity of the transform:
The most common approach to achieving this efficiency is to use a
decimation-in-time strategy that benefits from the non-linear
computational complexity of the transform:
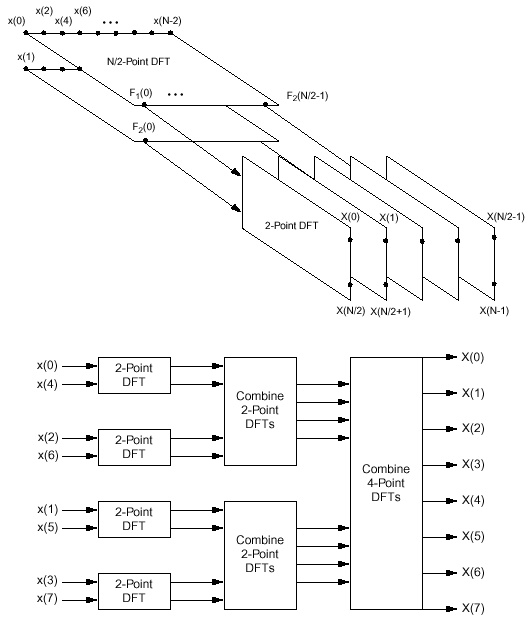
The Radix-2 and Radix-4 algorithms are extremely popular due
to their computational efficiency and relatively simple implementations:
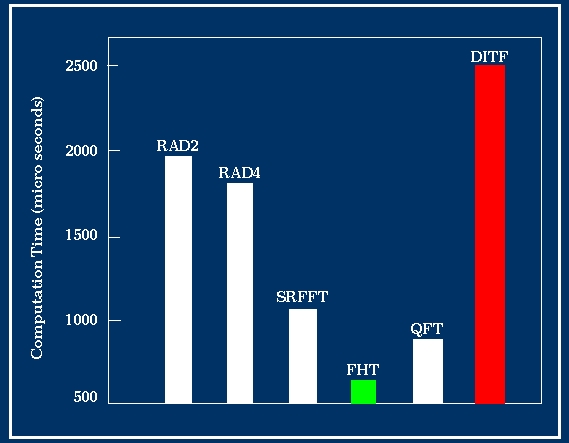
A definitive work on the computational complexity
of FFT algorithms, including benchmarks and software,
can be found at
parallel FFTs.



