MICROPHONE ARRAYS AND BEAM STEERING
Question: Can we improve performance using multiple microphones?
The goal of a microphone array is to localize a sound source by
directing a group of microphones to be most sensitive in a specific
direction. The procedure is completely analogous to analog antenna
theory.
 Steering of the array has several uses: increase SNR, direct
video in teleconferencing, enhance the human interface (hands-free).
Steering of the array has several uses: increase SNR, direct
video in teleconferencing, enhance the human interface (hands-free).
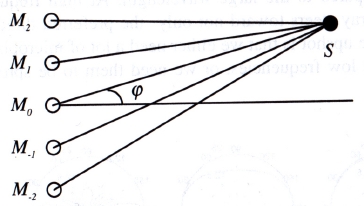
Steering the array amounts to adjusting the delays in each
microphone. The most common implementation is the delay
and sum beamformer:
 An example of a sensitivity pattern for this type of array is:
An example of a sensitivity pattern for this type of array is:
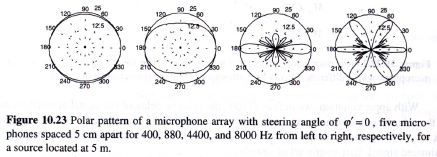 A 3D array can be used to localize sound to a single point in a room
(direction and distance). 2D arrays are most commonly used
to enhance SNR. Unfortunately, performance increases slowly
as a function of the number of microphones (1 dB rule). Hence,
this technology is impractical for many consumer applications.
A 3D array can be used to localize sound to a single point in a room
(direction and distance). 2D arrays are most commonly used
to enhance SNR. Unfortunately, performance increases slowly
as a function of the number of microphones (1 dB rule). Hence,
this technology is impractical for many consumer applications.
Two microphone versions of this idea based on adaptive filtering
are popular in automotive applications for noise suppression.



