- Hidden Markov Model
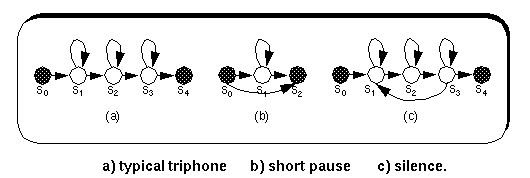
- Each HMM corresponds to an acoustic unit such as a phone or a syllable
- Output probability distributions are modeled by multi-variate
Gaussians
- Flexible algorithms are known which allow the HMMs to learn the
structure of the data during training in a relatively unconstrained
manner

